
Test MHA-1638
March 29, 2016
Go to all tests
Repeat of 1627, all birch.
Extra test #3 of matched load series to investigate PM repeatability with cordwood
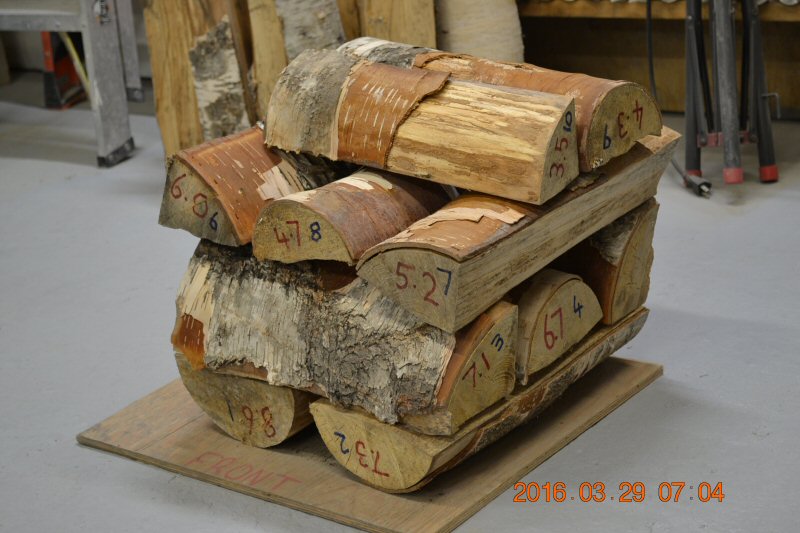
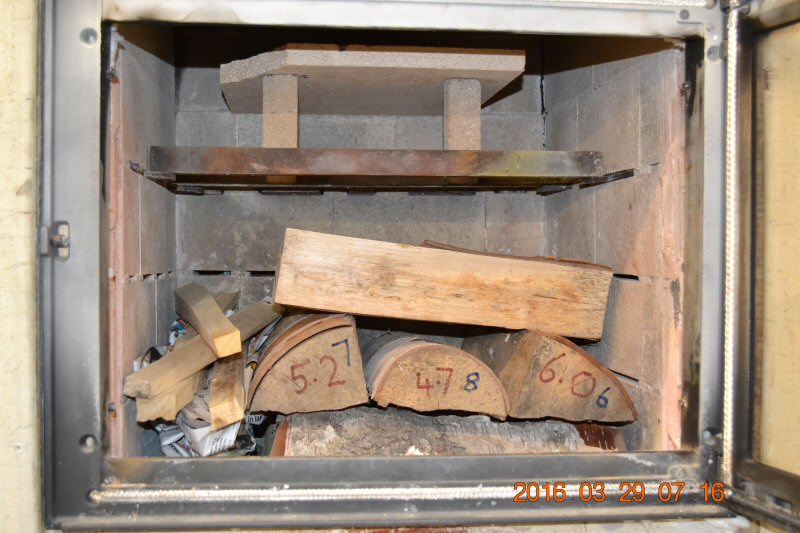
Log cabin stacking, side ignition,
63.0 lbs including 3.0 lbs kindling
15.0% moisture.
Baffle supports opened up. See MHA-1625
Air slots in firebox unblocked, except for top course (25% restriction)
See MHA-1623 for other modifications.
Original test + 6 matched loads + 1 extra test
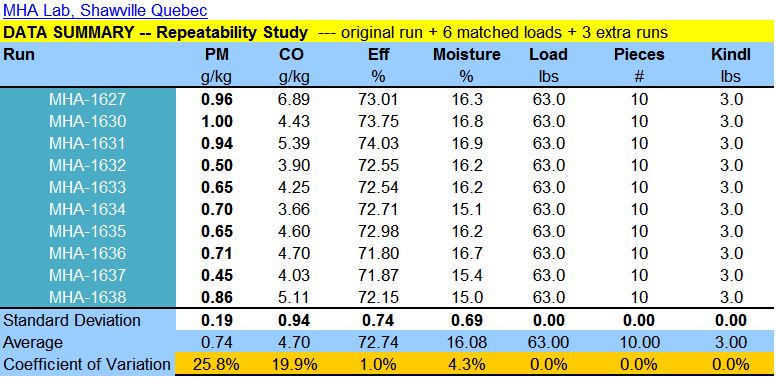
Coefficient of Variation (CV, or COV) is the standard deviation divided by the average.
25% COV means that on average a PM test number is accurate within +/- 25%
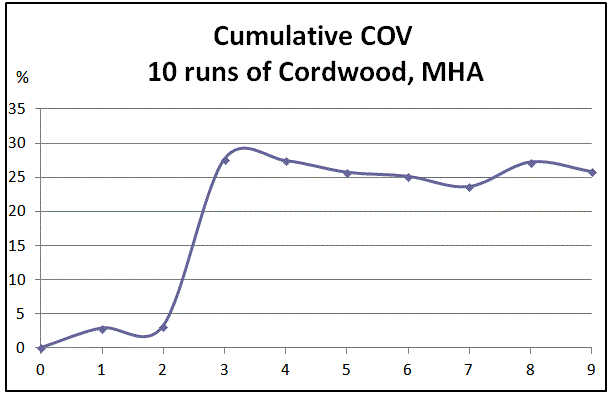
Cumulative coefficient of variation. After the first 3 tests, it looked like the COV was very tight, around 3%.
However, with more tests it settled to its realistic value, around 25%.
Compare with previous Lopez Labs crib repeatability testing, which yielded a COV of 10.2% with 4 sets of matched cribs (8 test runs)
Note
in the crib testing that the CO repeatability was much tigher, within
1.5%, although the CO value itself was about 8X higher than the
Eco-firebox.
In both cases, the efficiency was extremely tight.
Recently, MHA ran the Condar against Method M5G-3 on 3 pellets stoves (18 tests total) and achieved a COV of 3.1%
Compare with crib reproducibility (which is not the same as repeatability with the same operator within the same lab)
among different EPA accredited laboratories in round robin proficiency testing, running the official EPA M-28 test method
on the same stove, shipped to different laboratories, all using the M-28 specified Douglas Fir cribs at 4 different burn rates.
In an 18 year period, there were a total of 5 different stoves used.
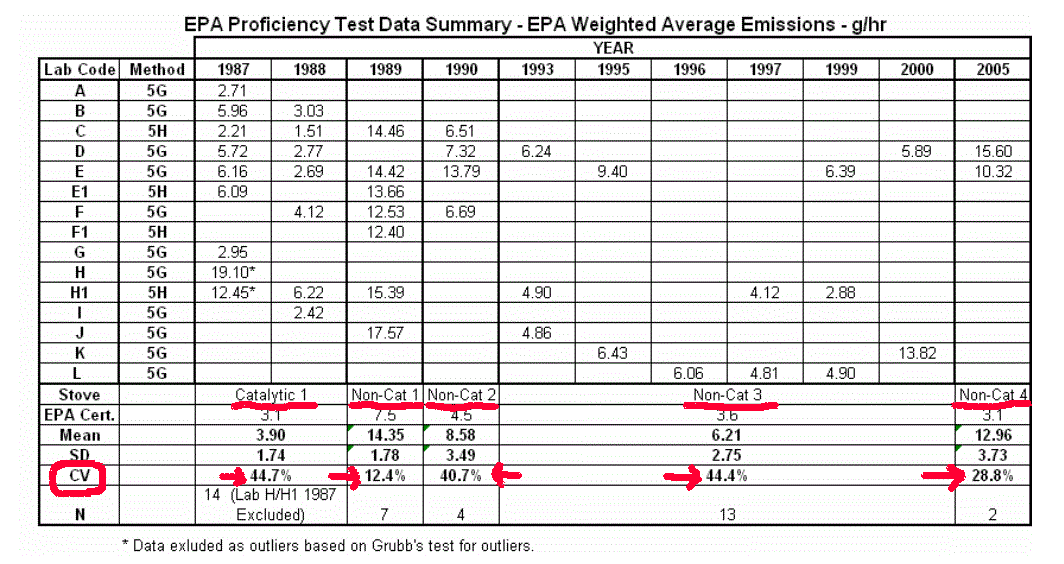
(table is excerpted from HPBA's NSPS submission)
With
some of the laboratories note the large variations in different
years, running exactly the same test on exactly the same stove.
Note the super dirty non-cat, in 1989, with very good reproducibility
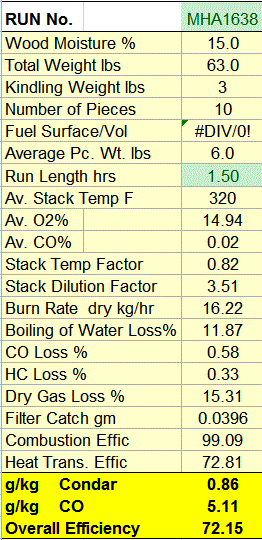 |
|
Condar summary
| |
Condar Spreadsheet
Raw Testo Data
Lab Notes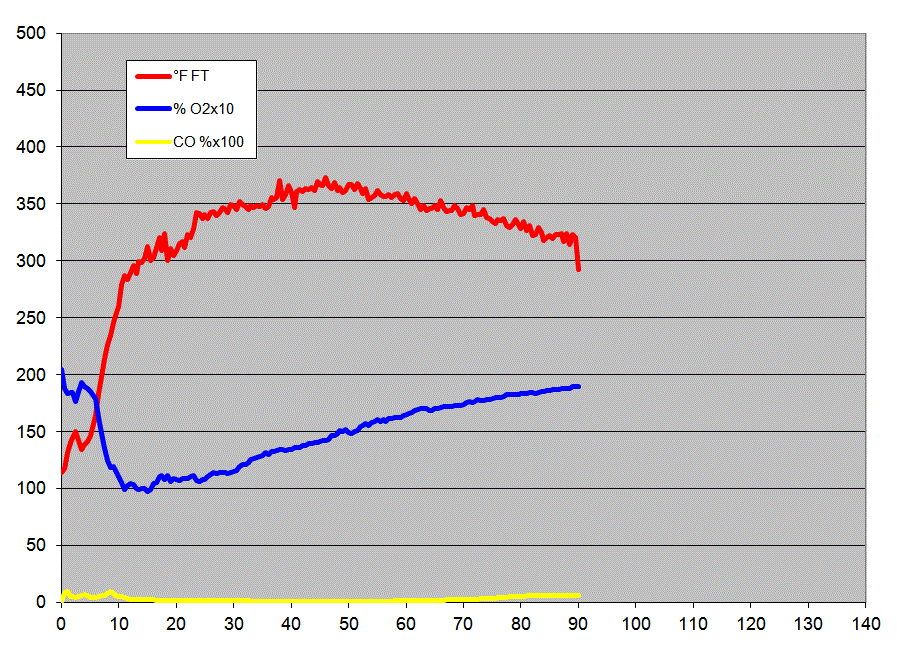
Gas graph. CO low was 62 ppm
Note the choppy stack temperature curve, due to wind.
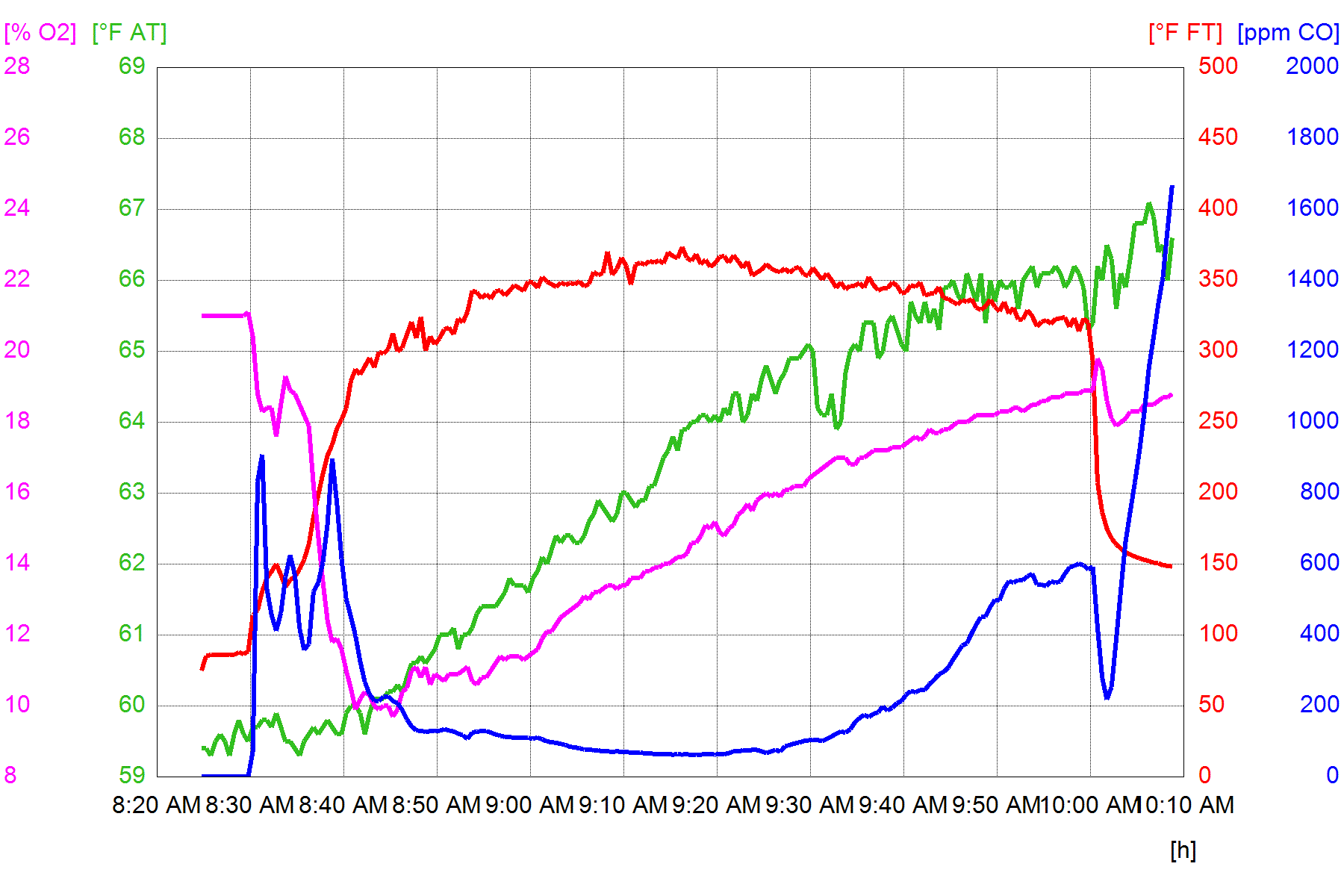
Testo gas graph.



This page was updated on March 31, 2016
This page was created on March 29, 2016


